ASP Classic Journeys: no-store
by Mauricio Rojas, on Mar 24, 2020 11:07:05 AM
While doing a migration from ASP Classic to ASP.NET we encountered some usages of the "no-store" CacheControl.
In ASP Classic the accepted values for CacheControl are:
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The .NET implementation only allows some values. Let's see the code for the .NET implementation:
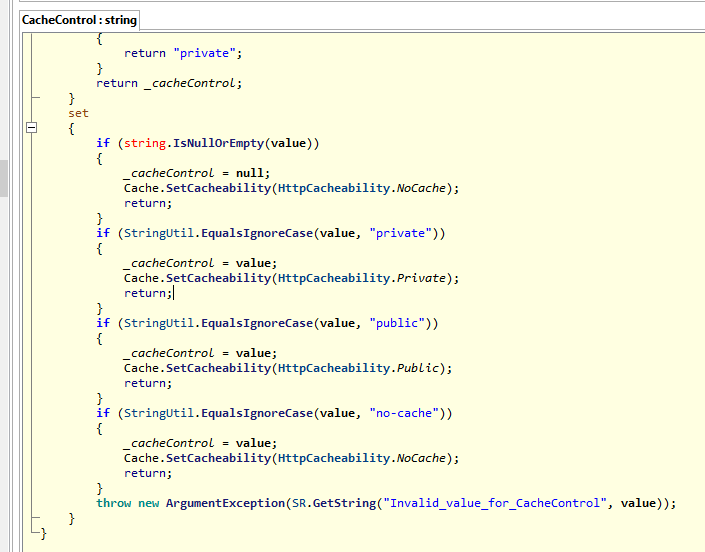
So that means that there is no direct equivalent of "no-store"
The closest equivalent can be achieved with code like:
Response.Cache.SetCacheability(HttpCacheability.NoCache);
Response.Cache.AppendCacheExtension("no-store, must-revalidate");
Response.AppendHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
Response.AppendHeader("Expires", "0");
The first line sets
Cache-control to no-cache, and the second line adds the other attributes no-store, must-revalidate.
